- +91 75677 63301
- 24*7 Emergency Care
Can A Hand Muscle Contusion Lead To Long-Term Stiffness
- Home
- /
- Muscle Tear
- /
- Can a hand muscle...
Our hands are among the most vital parts of our body—used for nearly every daily task, from eating and writing to working and expressing emotions. Because of their constant use and exposure, they are prone to injuries. One of the common hand injuries is a muscle contusion, also known as a bruise.
While most people recover from a bruise in a few days to weeks, some worry about whether such an injury could have lasting effects—particularly long-term stiffness. This article explores that question in depth.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding hand muscle contusions
A muscle contusion occurs when a sudden impact or blow damages muscle fibers and small blood vessels beneath the skin. This leads to bleeding under the skin and an accumulation of blood (hematoma), resulting in discoloration, pain, swelling, and tenderness.
In the hand, muscle contusions are relatively common because the hand has less protective soft tissue compared to other body parts, leaving bones, muscles, and tendons more vulnerable.
- Sports injuries. (e.g., a direct hit from a ball, fall during contact sports)
- Accidental falls. (landing on the hand or striking a surface)
- Workplace injuries. (machinery accidents, heavy lifting trauma)
- Everyday accidents. (closing a door on the hand, hitting a hard object)
The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the force of the impact and the extent of tissue damage. Common signs include:
- Localised pain and tenderness.
- Swelling around the injured site.
- Bruising or skin discoloration. (blue, purple, green, or yellow over time)
- Restricted movement of the fingers or wrist due to pain.
- A feeling of tightness or pressure in the hand.
Mild cases heal quickly, while more severe ones may take weeks and could cause complications if not treated correctly.
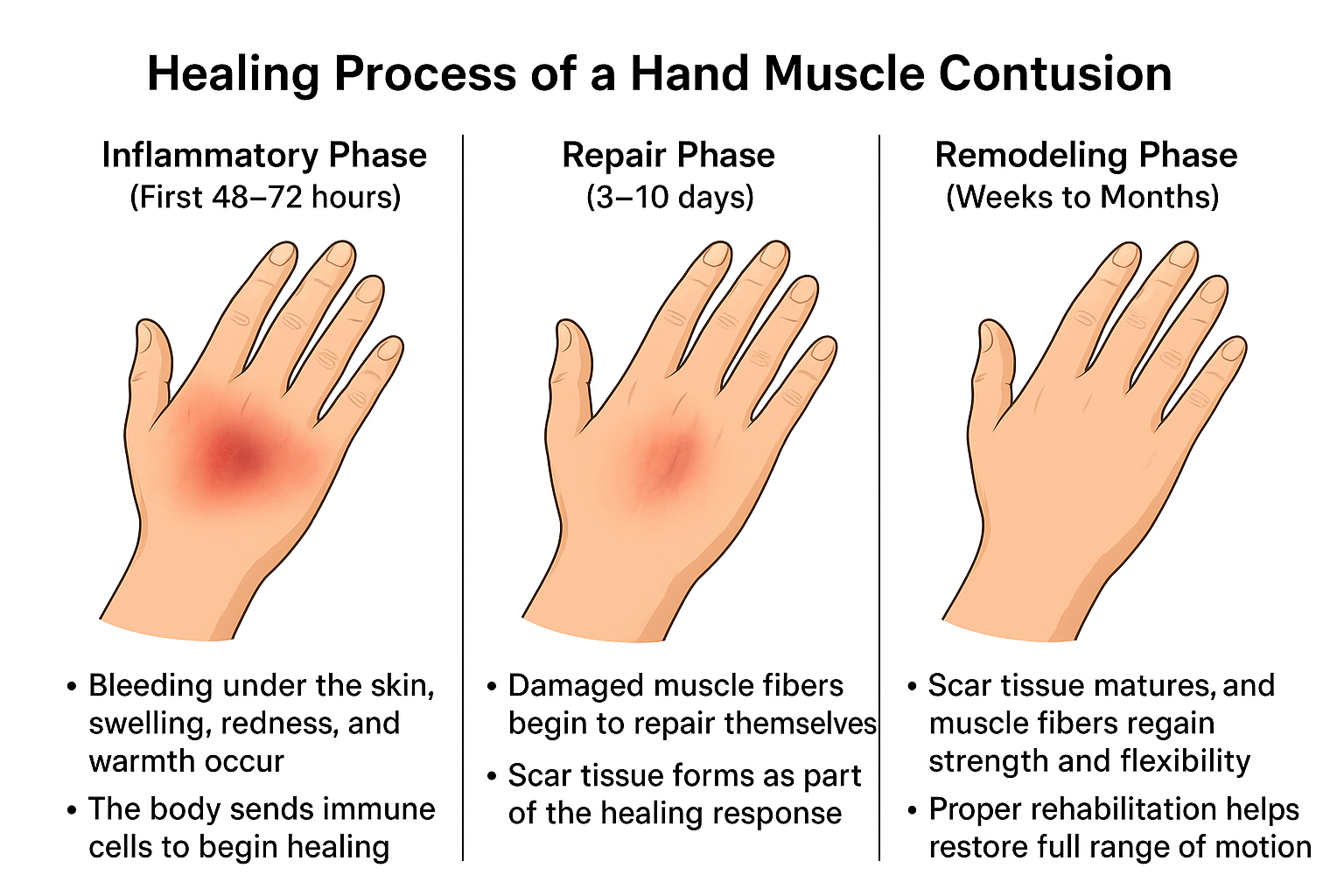
The natural recovery process involves several stages:
- Inflammatory Phase (First 48–72 hours)
- Bleeding under the skin, swelling, redness, and warmth occur.
- The body sends immune cells to begin healing.
- Bleeding under the skin, swelling, redness, and warmth occur.
- Repair Phase (3–10 days)
- Damaged muscle fibers begin to repair themselves.
- Scar tissue forms as part of the healing response.
- Damaged muscle fibers begin to repair themselves.
- Remodeling Phase (Weeks to Months)
- Scar tissue matures, and muscle fibers regain strength and flexibility.
- Proper rehabilitation helps restore full range of motion.
- Scar tissue matures, and muscle fibers regain strength and flexibility.
If this process is interrupted—by overuse, lack of movement, or complications—stiffness may persist.
The short answer is: Yes, it can, but rarely. Most hand contusions heal without lasting issues. However, several factors can increase the risk of chronic stiffness:
- Severe Tissue Damage – Deep contusions that extend into muscle, tendon, or joint structures take longer to heal. Prolonged recovery may lead to adhesions and stiffness.
- Excessive Scar Tissue Formation – When the body repairs muscle fibers, it produces scar tissue. If too much forms or it attaches abnormally to surrounding tissues, flexibility may be reduced.
- Compartment Syndrome – In rare, severe cases, swelling inside the tight compartments of the hand can block blood flow. If not treated urgently, it may cause muscle death and permanent stiffness.
- Joint Involvement – If the contusion extends to nearby joints, inflammation can limit movement, and prolonged immobility may lead to stiffness.
- Improper Healing & Immobilization – Keeping the hand completely still for too long (out of fear of pain) can cause joints and soft tissues to stiffen. Gentle early movement is important.
- Delayed or No Treatment – Ignoring a significant hand injury may result in complications like chronic pain, stiffness, or even reduced hand function.
- Patient Factors
- Age – older individuals may have slower healing.
- Health conditions – diabetes, poor circulation, or connective tissue disorders can delay healing.
- Lifestyle – smoking and poor nutrition impair tissue recovery.
Warning signs: When to see a doctor
You should consult a doctor if you notice:
- Severe or worsening swelling and bruising.
- Inability to move fingers or grip objects.
- Persistent stiffness beyond 2–3 weeks.
- Numbness or tingling in the hand.
- Signs of infection. (fever, warmth, pus, redness)
Your doctor may recommend X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI to rule out fractures, ligament/tendon damage, or complications.
Prognosis: Is stiffness permanent?
- Mild to moderate contusions → usually heal within 2–3 weeks with no stiffness.
- Severe contusions with complications → may take months and need rehabilitation.
- Rare cases with compartment syndrome or tendon damage → may result in some long-term stiffness, though therapy can often improve function.
In most cases, long-term stiffness is preventable if the injury is recognized early and managed properly.
Conclusion
A hand muscle contusion may seem like a minor injury, but when not managed correctly, it can sometimes lead to long-term stiffness due to scar tissue, joint involvement, or prolonged immobility. Thankfully, this outcome is uncommon and largely preventable.
The key is early care, gentle movement, and medical supervision when necessary. If stiffness does develop, physiotherapy and rehabilitation play a vital role in restoring hand mobility.
Your hands are essential for your independence and quality of life—never ignore an injury that doesn’t heal as expected. Seeking professional care ensures the best recovery and minimizes the risk of permanent stiffness. At Krisha Hand Hospital, our team of specialists is dedicated to providing advanced treatment and rehabilitation for hand injuries. If you’re experiencing pain, stiffness, or slow recovery after a hand contusion, book a consultation today and take the first step toward regaining full function.
Author bio
Dr. Karn Maheshwari is the founder of Krisha Hand Hospital, Ahmedabad, established in 2016. He is the only fnb-qualified hand surgeon across Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.
With MS and DNB in orthopedics, Dr. Maheshwari specializes in treating a wide range of hand and wrist conditions, including carpal tunnel syndrome, sports hand injuries, orthopedic hand surgery, ganglion cysts, mangled hand injuries, congenital hand differences, brachial plexus palsy, cerebral palsy & spastic hand, hand tendinopathy, hand microsurgery, hand swelling, hand transplants, hand reimplantation, rheumatoid hand deformities, and peripheral nerve injuries & compressive neuropathies.
Dr. Maheshwari’s unmatched expertise and patient-centric approach ensure world-class treatment, advanced surgical solutions, and optimal recovery for patients with complex hand and wrist conditions.
FAQs
Mild contusions may allow light activity within a few days, while severe cases may require 2–3 weeks of limited use. Always follow your doctor’s advice.
Yes. Severe bruising and swelling can mimic a fracture or ligament injury. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRI are often needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Children generally heal faster than adults, but if proper care isn’t taken, they can also develop stiffness, especially if the injury involves growth plates or joints.
Gentle massage, once swelling subsides, can improve circulation and flexibility. However, aggressive massage early on may worsen bleeding and swelling.
Yes. A diet rich in protein, vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc supports tissue healing and reduces recovery time.
In rare cases, deep contusions may compress nearby nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, or weakness. Persistent symptoms require medical attention.
Yes, due to repeated trauma and early return to activity, athletes may have a higher risk if proper rest and rehabilitation are neglected.