- +91 75677 63301
- 24*7 Emergency Care
Most common sports injuries of the hand and How to prevent them?
- Home
- /
- Hand Surgery
- /
- Types of hand fractures...

Hand fractures are among the most common injuries treated by orthopedic and hand specialists. The hand is a complex structure made up of 27 small bones, and a fracture in any of them can significantly impact function and movement. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment are essential to restore hand function, promote healing, and prevent long-term complications.
In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of hand fractures and how each is commonly treated.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a hand fracture?
A hand fracture is a break or crack in one or more bones of the hand. These fractures may affect:
- Phalanges – the bones of the fingers.
- Metacarpals – the bones in the palm.
- Carpals – the small bones of the wrist.
Hand fractures can result from falls, sports injuries, accidents, or direct trauma such as punching a hard object.
Common types of hand fractures
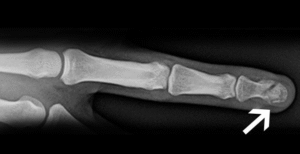
- Common cause: Slamming a finger in a door, crushing injuries.
- Symptoms: Swelling, tenderness, bruising at the fingertip.
- Treatment: Splinting or, in some cases, surgical fixation if bone fragments are displaced.
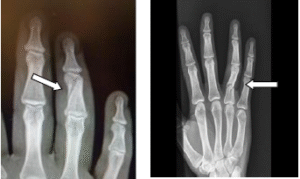
- Cause: Sports injuries, machinery accidents.
- Symptoms: Deformity, swelling, limited finger motion.
- Treatment: Immobilization with splints or surgery if the fracture is unstable or involves a joint.
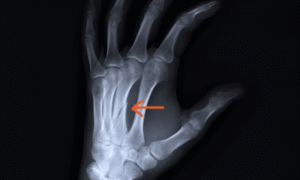
- Types include:
- Boxer’s fracture – fracture of the 5th metacarpal. (little finger)
- Bennett’s fracture – base of the thumb metacarpal.
- Boxer’s fracture – fracture of the 5th metacarpal. (little finger)
- Symptoms: Swelling, hand deformity, reduced grip strength.
- Treatment: May include splinting, casting, or surgical fixation with plates, screws, or pins.
4. Carpal bone fractures (Wrist bones)
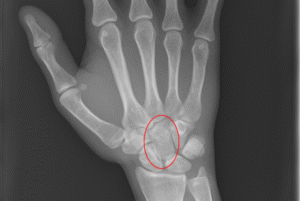
- Most common: Scaphoid fracture.
- Cause: Fall on an outstretched hand.
- Symptoms: Pain and swelling at the base of the thumb.
- Treatment: Immobilization in a cast or surgical screw fixation.
5. Intra-Articular fractures
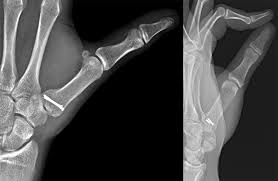
- Definition: Fractures that extend into a joint space.
- Significance: Higher risk of long-term stiffness or arthritis.
- Treatment: Often require surgery to align the joint surfaces precisely.
Signs you may have a hand fracture
- Swelling and bruising.
- Deformity or visible bump.
- Difficulty moving fingers or gripping.
- Numbness or tingling.
- Pain that worsens with movement or touch.
If you suspect a fracture, it’s crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible to prevent improper healing.
How are hand fractures diagnosed?
Physical examination:
- Assess for swelling, bruising, or deformity.
- Check for tenderness over specific bones.
- Evaluate range of motion and grip strength.
- Look for signs of nerve or tendon injury.
X-rays:
- First-line imaging to confirm the presence of a fracture.
- Helps determine the type. (displaced, non-displaced, comminuted, etc.)
- Shows fracture alignment and involvement of joints.
CT Scan:
- Offers detailed, cross-sectional images of complex fractures.
- Useful for planning surgical intervention, especially in wrist or joint fractures.
MRI Scan:
- Helpful in detecting soft tissue injuries along with fractures.
- Used when ligament or tendon damage is suspected.
- Can identify subtle fractures not visible on X-rays.
Other tests (if needed):
- Bone scan – occasionally used for stress fractures or hairline fractures.
- Ultrasound – sometimes used to assess soft tissue involvement in children.
Treatment options for hand fractures
Non-Surgical treatment
- Immobilization: Using splints or casts to keep the bones aligned.
- Buddy Taping: Taping a fractured finger to an adjacent one for support.
- Pain management: Anti-inflammatory medications.
Surgical treatment
- Required when:
- Bones are displaced.
- The fracture involves a joint.
- There are multiple or open fractures.
- Bones are displaced.
- Procedures may include:
- Internal fixation (plates, screws, wires)
- External fixation (pins and external devices)
- Internal fixation (plates, screws, wires)
- Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy plays a key role in restoring strength and mobility post-surgery
Why choose Krisha Hand Hospital?
At Krisha Hand Hospital, we offer:
- Super-specialized care in hand and wrist injuries.
- Experienced hand surgeons and orthopedic experts.
- Advanced diagnostic and surgical technologies.
- Personalized rehabilitation plans.
Your hands deserve expert care — and we’re here to help you heal with precision and compassion.
Conclusion
Understanding the type of hand fracture and receiving the right treatment at the right time can make a major difference in your recovery and long-term hand function. Whether it’s a minor fracture or a complex break involving joints or tendons, accurate diagnosis and expert care are essential to avoid long-term stiffness, weakness, or deformity.
At Krisha Hand Hospital, we specialize in comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of all types of hand fractures. From advanced surgical techniques to customized rehabilitation plans, our goal is to restore your hand’s strength, movement, and functionality. If you or a loved one has suffered a hand injury, book a consultation with our expert team today and take the first step toward a complete recovery.
Author bio
Dr. Karn Maheshwari is the founder of Krisha Hand Hospital, Ahmedabad, established in 2016. He is the only fnb-qualified hand surgeon across Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.
With MS and DNB in orthopedics, Dr. Maheshwari specializes in treating a wide range of hand and wrist conditions, including carpal tunnel syndrome, sports hand injuries, orthopedic hand surgery, ganglion cysts, mangled hand injuries, congenital hand differences, brachial plexus palsy, cerebral palsy & spastic hand, hand tendinopathy, hand microsurgery, hand swelling, hand transplants, hand reimplantation, rheumatoid hand deformities, and peripheral nerve injuries & compressive neuropathies.
Dr. Maheshwari’s unmatched expertise and patient-centric approach ensure world-class treatment, advanced surgical solutions, and optimal recovery for patients with complex hand and wrist conditions.
FAQs
Healing time depends on the type and severity of the fracture, but most hand fractures heal within 3 to 6 weeks. Complex fractures or those requiring surgery may take longer.
This depends on which hand is injured, the severity of the fracture, and your type of work. In general, you should avoid activities that strain or stress the hand until your doctor approves.
In many cases, yes. Even with non-surgical treatment, physical therapy is often necessary to regain strength, mobility, and coordination.
Yes, children and older adults are more prone to hand fractures due to sports injuries and falls, respectively.
Untreated fractures can lead to malunion (bones healing in the wrong position), stiffness, chronic pain, weakness, or even permanent loss of hand function.
Yes, especially if the fracture involves a joint (intra-articular fracture) or is not properly aligned. Long-term complications may include post-traumatic arthritis.
